
The TLS protocol works on two layers where the TLS record protocol provides security to connections. TLS still provides backward compatibility for older devices. Thus, TLS provides support with remote passwords, elliptical curve keys and pre-shared keys which are not supported by SSL.
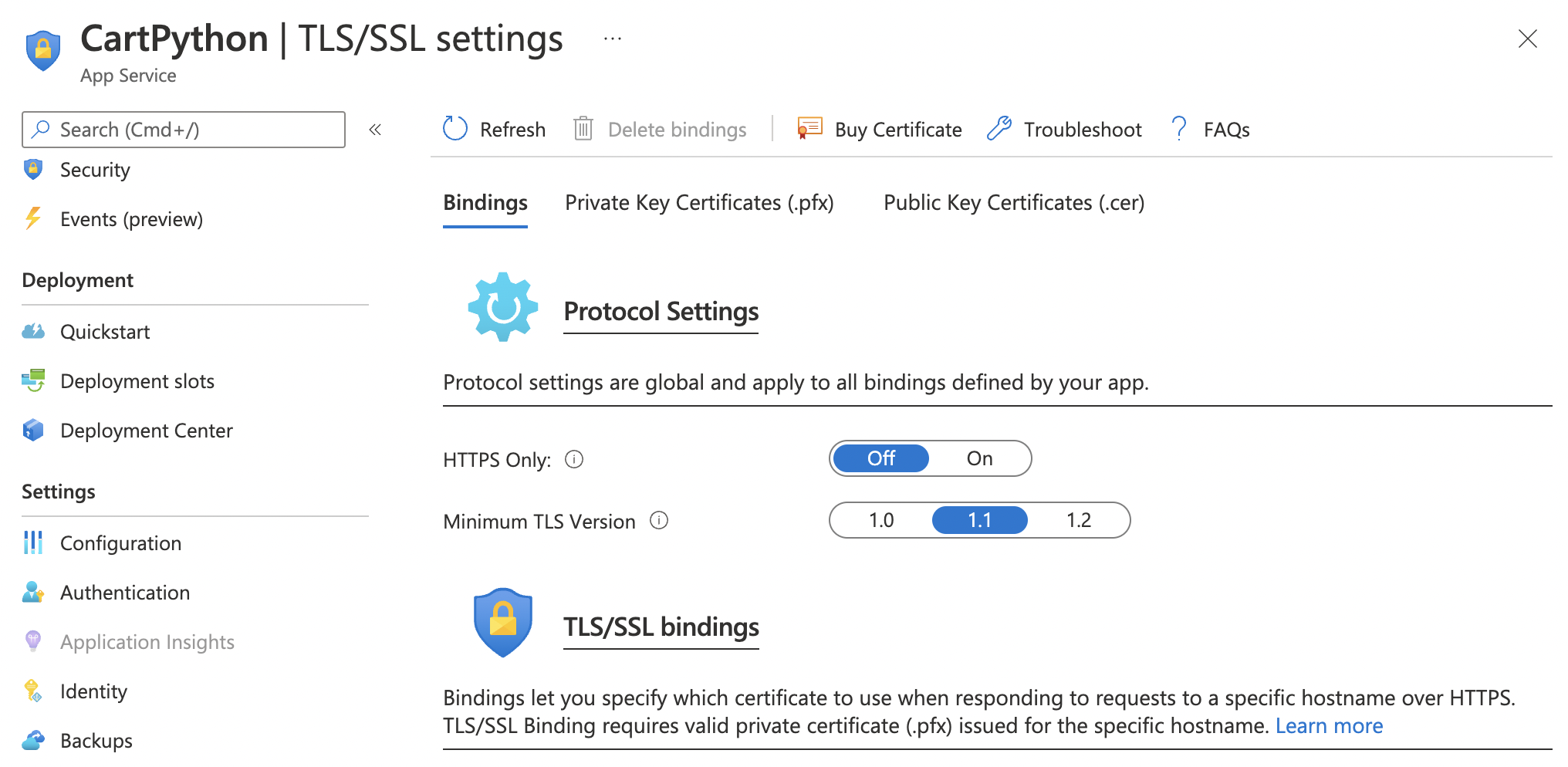
TLS provides a more robust message authentication system, key material generation along other encryption algorithms when compared to SSL. TLS 1.2 is the most widely deployed protocol version.

TLS 1.0 and 1.1 have been “broken” and are deprecated as of March 2020.TLS is also a cryptographic protocol that provides secure communication between web server and client via implicit connections.Four versions of TLS have been released: TLS 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, and 1.3.The first version of TLS was developed by the Internet Engineering Taskforce (IETF) in 1999.TLS stands for “Transport Layer Security.” All versions of SSL have been found vulnerable, and they all have been deprecated.Three versions of SSL have been released: SSL 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0.SSL is a cryptographic protocol that uses explicit connections to establish secure communication between web server and client.Netscape developed the first version of SSL in 1995.openssl s_client -connect :443 -tls1_3.openssl s_client -connect :443 -tls1_2.openssl s_client -connect :443 -tls1_1.The following commands can be used to find TLS version: OpenSSL command is the easiest way to check TLS version. It is a descendent of SSL and is regarded to be more powerful and effective. TLS 1.3 is the latest version of the TLS protocol. Both SSL and TLS protocols aim to protect sensitive information used during transactions such as payment processing that requires authentication to prove the identity of our server to the users.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
